In vivo thrombolytic effect of oral NKCP in experimental thrombolysis model
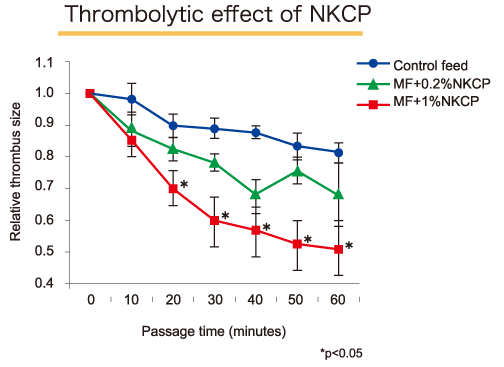
The thrombolytic effect of NKCP on rat model was observed in a 14 week study. The NKCP was evaluated in two groups, in a mix of 0.2% and 1% in feed, as compared to a control group. Thrombolysis was evaluated using a He-Ne laser induced thrombosis model in mesenteric microvessels. The size of the artificially produced thrombus was measured from the time of formation to evaluate the thrombolytic effect of NKCP.
Thrombolytic activity clearly increased dose-dependently in the NKCP treatment groups compared with the control group. There was an 82% decrease in thrombus volume in the control group, as compared to 67% decrease in the 0.2% NKCP group, and a 51% decrease (statistically significant) in the 1% NKCP group. The extent of thrombolysis in the 1% group was equivalent to that seen in animals treated with a bolus intravenous infusion of 0.2mg/kg of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA).
Based on the body weight and feed intake of rats used in the study, the dose of NKCP was calculated to be about 160mg/kg/day for the 0.2% NKCP feed and 800mg/kg/day for the 1% NKCP feed.
Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 2003; 33: 138-143
